Johkasou – In Site Compact Waste Water Purification Tanking System
Description
Johkasou in Japanese language means, purification Tank. Johkasou products are approved by the government of Japan and are extensively deployed across Japan as a part of government policy. As a matter of fact, more than 26% of Sewage in Japan is treated through Johkasou systems. Over 8 million Johkasou are running successfully in Japan and several millions are installed in various other countries.
Johkasou system is regulated by the Johkasou Act, in which technical standards for its manufacturing, installation, and operation & maintenance including desludging are stipulated. The Act also stipulated a qualification system for Johkasou related technicians. In addition, Johkasou act stipulates each Johkasou product to pass the performance evaluation test before putting the product in the market. Furthermore, in Japan the sludge generated from Johkasou is appropriately treated at night soil treatment facility before used as fertiliser or industrial fuel.
This way Johkasou can play the role of a wastewater treatment facility to become a system that integrates the technology and its management, which is useful for both mankind and environment.

Core Concept of Johkasou is to treat domestic waste water locally and reuse it locally, which is very appropriate for Sri Lanka in current circumstances.
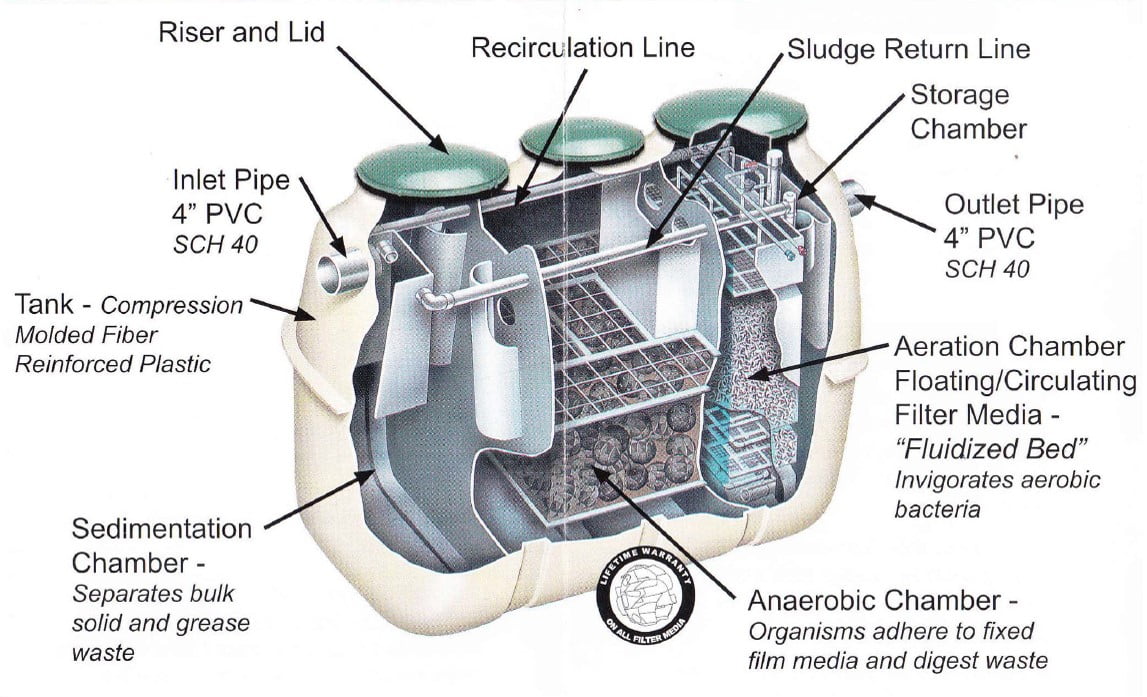
- Johkasou, which can be installed underground or above ground as a single compact tank.
- It contains five functional chambers

- It is equipped with an anaerobic & aerobic combined biological treatment process.
- Noise & Odour free system.
- This technology, which is used in this treatment plant, is equivalent to that of a centralized public sewage plant.
- Various types and sizes are available,
CE5, CE7, CE10, CE14, CE18, CE21, etc. - FujiClean’s highly advanced models are now available all over the world, especially in Australian, European and North American markets.

Methodology
COLLECTION TANK
- Sewage Waste Water & Urinal Waste Water generated from toilets and washing waste water from wash basins will be collected into a main collection tank after passing through a Screen Chamber.
- Then collected waste water will be pump to the treatment plant from time to time according to the waste water generation rate.
EQUALISATION TANK
- To make a homogeneous mixture of effluent.
- To equalize and regulate the flowrate.
- Further it acts as Anerobic reactor (Anerobic media & bacteria are included)
- From Anerobic reactor, reduce most amount of COD in waste water by converting to methane & very little amount of COD is converted to sludge.
- 60% of total BOD will be removed in Anerobic filters.
AERATION TANK
- For this process, air should be supplied continuously for the Aerobic Bacteria (air consuming) to digest the dissolved organics in Waste, thus makes the waste water clean.
- The process inside the Aeration Tank is called as “Activated Sludge” treatment.
- Removal of remaining organic matter (BOD) is done by Aerobic Bacteria, which is living in the reactor.
SEDIMENTATION TANK
- Dead bacteria (Sludge) flowing in waste water will be settled and removed from the process as wasted sludge to produce a cleaner effluent.
- Some part of the settled sludge will be repumped to the Aeration tank to continue activated sludge process.
- Separated water layer will be sent out for further processing.
SLUDGE TANK
- This is used to collect waste sludge emanating from the Sedimentation tank.
- This collected sludge will be removed time to time by gully sucker, approximately 02 times per year.
- Some amount of sludge will be repumped to the EQ tank from here.
SAND FILTER
- To remove possible solid matter from the Sedimentation tank effluent.
CARBON FILTER
- To polish further treated water, which is coming from the sand filter
CHEMICAL DISINFECTION
- Before discharging the treated water to the environment, it should be disinfected to kill the remaining active bacteria and neutralize the treated water.
FINAL DISCHARGE
- Treated water will be collected into a treated water collection tank first.
- Then it will be directed to a soakage pit after passing through a flower pond.